In the credit repair world, trust is vital for both companies and customers. Thus, regulatory measures are in place to uphold this trust, with the surety bond playing a key role. Understanding these surety bonds is crucial whether you’re a credit repair business or hiring their services.
Let’s explore credit repair surety bonds, why they matter, and how they affect businesses and customers. We’ll also delve into the steps of getting surety bonds for credit repair businesses.
You may use these links to easily navigate to the article’s content:
What is a Surety Bond?
A surety bond is a legally binding agreement between three parties: the principal, the obligee, and the surety. This agreement serves as a protective measure to ensure accountability and compliance within the industry. Let’s explore each party in more detail.
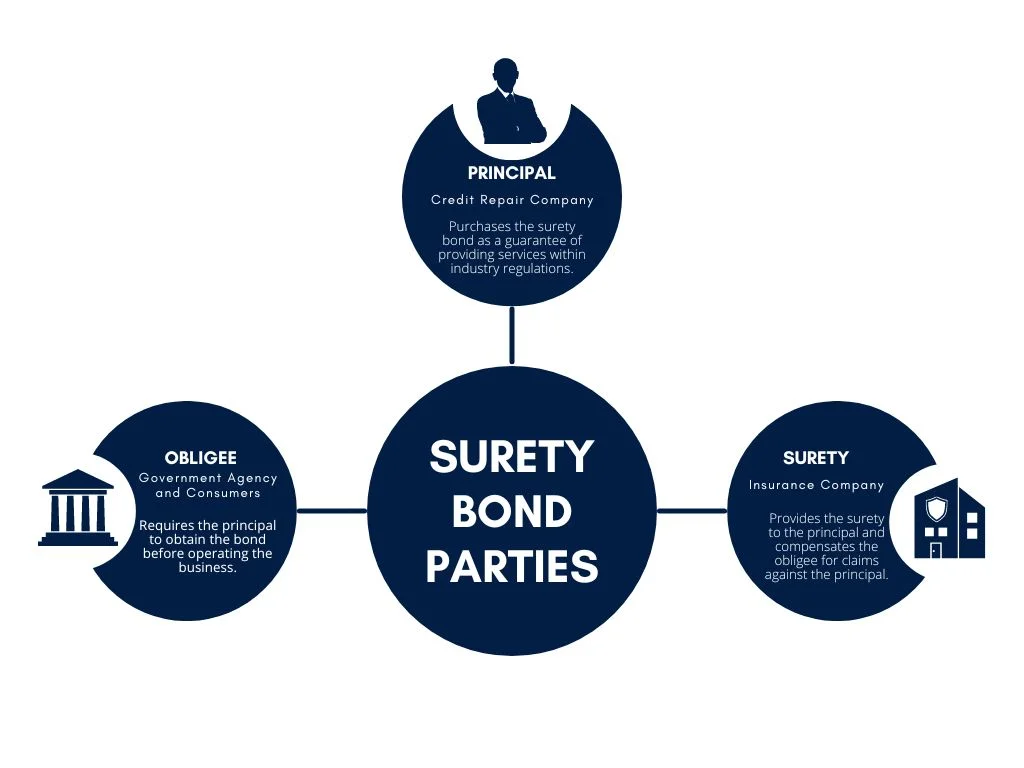
The Principal
Firstly, the principal, which in this case is the credit repair business. This party obtains a surety bond to demonstrate its commitment to providing credit repair services ethically and within industry regulations. By acquiring a surety bond, the credit repair business pledges to fulfill its responsibilities to clients and adhere to the standards set forth by regulatory authorities.
The Obligee
Secondly, the obligee, who can be either the regulatory authority overseeing credit repair practices or the consumer seeking credit repair services. This party relies on the surety bond as a form of protection. For regulatory agencies, the surety bond serves as a financial guarantee that the credit repair business will conduct its operations by laws and regulations. Similarly, for consumers, the bond ensures they get compensation if the credit repair company breaches the contract or acts improperly.
The Surety
Finally, the surety, typically a bonding company. This party is the intermediary responsible for underwriting the bond and providing financial backing. The surety evaluates the principal’s creditworthiness and reliability before issuing the bond. If the principal fails to fulfill its obligations, the surety assumes responsibility for compensating the obligee up to the bond’s predetermined limit.
Overall, a surety bond offers peace of mind to all parties involved by establishing a framework of accountability and financial security.
Role and Importance of Surety Bonds in Credit Repair Businesses and Consumers
Surety bonds are pivotal in ensuring transparency, integrity, and accountability within the credit repair industry. For credit repair businesses, these bonds serve as a badge of credibility, instilling confidence in clients and regulatory authorities.
Credit repair service bonds also provide financial protection for consumers if the credit repair company fails to fulfill its obligations or engages in misconduct. This assurance is invaluable for consumers, as it mitigates the risk of financial loss or harm.
Regulatory Requirements for Credit Repair Surety Bonds
Regulatory requirements for credit repair surety bonds are crucial for maintaining the industry’s integrity and protecting consumers. Government bodies or regulatory agencies establish and enforce these requirements to govern the operations of credit repair businesses. These ensure that credit repair companies comply with standards of conduct and possess the financial resources to fulfill their obligations.
One key aspect of these requirements involves determining minimum bond amounts, which are set to guarantee that credit repair companies have enough funds to compensate clients in case of wrongdoing. Additionally, regulatory criteria may dictate that credit repair businesses obtain surety bonds from licensed bonding companies, further ensuring reliability and consumer protection.
Furthermore, regulatory authorities may impose specific conditions on credit repair businesses related to surety bonds. Such as conducting background checks on key personnel or maintaining adequate financial reserves. These conditions promote transparency, accountability, and ethical behavior within the industry. Therefore, ultimately fostering consumer trust and confidence in credit repair services.
However, it’s important to note that the amount of a credit repair bond differs from state to state, and not all states require a surety bond. Navigate to this map to check if your state requires one for credit repair companies.
How Much are Credit Repair Surety Bonds?
The cost of credit repair service bonds can vary significantly depending on several factors, including the bond amount required in the state, the creditworthiness of the credit repair business, and the bonding company issuing the bond. Generally, credit repair surety bond premiums are calculated as a percentage of the bond amount.
On average, credit repair bond premiums typically range from 1% to 15% of the total bond amount. For example, if the required bond amount is $10,000, the premium could range from $100 to $1,500 annually, depending on the specific circumstances.
Resource: NNA Surety Bonds
Surety Bond Claims Against Credit Repair Services
Surety bond claims in credit repair are a vital recourse mechanism for consumers and regulatory authorities in cases of non-performance, malpractice, or breaches of contract by credit repair businesses.
When a consumer believes that a credit repair company has failed to fulfill its obligations or has engaged in misconduct, they can file a claim against the surety bond. This initiates a process wherein the surety company investigates the claim to determine its validity and assess the extent of the damages incurred. If the claim is found to be legitimate and within the scope of the bond coverage, the surety may compensate the aggrieved party up to the bond’s predetermined limit.
Hence, surety bond claims help mitigate the risks associated with credit repair services. And ensure that consumers have avenues for seeking redress in cases of fraud, negligence, or misconduct.
Moreover, surety bond claims serve as a deterrent against unethical behavior within the credit repair industry. Credit repair businesses understand that their surety bonds are at stake and that they may face financial consequences for failing to meet their obligations to clients and adhere to industry standards.
Steps on How to Apply for Credit Repair Surety Bond?
Applying for a credit repair surety bond involves several steps. Below is a general outline of the process:
1. Understand the Requirements
Familiarize yourself with the specific requirements for credit repair surety bonds in your jurisdiction. Each state or locality may have its own regulations regarding bonding amounts and procedures.
2. Find a Reputable Surety Bond Provider
Look for a reputable surety bond provider or agency that offers credit repair surety bonds. You can search online or ask for recommendations from other professionals in your industry.
3. Gather Necessary Information
Prepare the required information and documentation. This may include personal information such as your social security number, financial statements, business details, and other relevant documentation.
4. Complete the Application
Fill out the application form provided by the surety bond provider. Make sure to provide accurate and complete information to avoid delays in the approval process.
5. Submit Required Documentation
In addition to the application form, you may need to submit additional documentation such as proof of business registration, financial statements, and any other documents required by the surety bond provider.
6. Undergo Underwriting
Once you’ve submitted your application and documentation, the surety bond provider will review your information and assess your risk profile. This process is known as underwriting. Depending on your creditworthiness and other factors, the provider will determine the terms of the bond, including the premium rate.
7. Pay the Premium
If your application is approved, you must pay the premium for the credit repair surety bond. The premium is typically a percentage of the total bond amount and is paid annually.
8. Receive the Bond
After payment of the premium, the surety bond provider will issue the bond. You will receive a copy of the bond. In some cases, the original bond may be sent directly to the obligee (the entity requiring the bond, such as a government agency).
9. Maintain Compliance
Once you have obtained the credit repair surety bond, you must comply with all relevant laws and regulations governing your industry. Failure to do so could result in a claim being filed against your bond.
10. Renew the Bond
Credit repair surety bonds must be renewed annually. Keep track of the renewal date and submit any required documentation or payments on time to maintain your bond in good standing.
Disclaimer: This is not a legal advice. It’s essential to consult with a surety bond professional or legal advisor for specific guidance tailored to your circumstances and state.
In conclusion, credit repair surety bonds are a cornerstone of accountability and consumer protection within the credit repair industry. These bonds play a vital role in upholding industry standards and regulatory compliance by providing financial assurances and fostering trust among stakeholders. For credit repair businesses and consumers, understanding the intricacies of surety bonds is essential for navigating the complexities of the credit repair landscape and ensuring a safe and transparent environment for all parties involved.
Are you running a credit repair company?
The credit repair software that doesn’t lie to you.
*Automates 90% of the business process
*Process a client in just 15 seconds
*Auto assigns dispute letters, reasons, and types
*Complete with tools you need to run a business (CRM, Sales, and Marketing programs)
*AI text generator for your writing needs
*Internal invoicing system
*And so much more.
You can also book a live presentation with us to meticulously see all the amazing features and ask our expert any questions you may have. It’s free and 100% no-pressure!
For credit repair business start-ups, I recommend learning about credit repair laws to avoid legal issues and a guide on how to start credit repair business. Additionally, if you want to maximize your income by being a credit repair service outsource provider, we also have a program for you.
Frequently Asked Questions About Surety Bonds
1. What is a surety bond, and how does it work?
A surety bond is a three-party agreement where the surety (bonding company) guarantees to the obligee (the party requiring the bond) that the principal (the party obtaining the bond) will fulfill certain obligations. If the principal fails to meet these obligations, the surety compensates the obligee, and the principal reimburses the surety.
2. Why do I need a surety bond?
Surety bonds are often required by government agencies or private entities as a form of protection against financial loss or misconduct. They provide assurance that the credit repair company will follow the credit repair laws, fostering trust and credibility in business transactions.
3. How much does a surety bond cost?
The cost of a surety bond, known as the premium, varies based on factors such as the bond amount, the applicant’s credit history, and the type of bond required. Premiums typically range from 1% to 15% of the bond amount annually, but this can vary significantly depending on individual circumstances.
4. What happens if I don’t fulfill my obligations under the bond?
If the principal fails to fulfill their obligations under the bond, the obligee can make a claim against the bond to recover financial losses. The surety may investigate the claim and, if valid, compensate the obligee up to the bond amount. The principal is then responsible for reimbursing the surety for any claims paid out.

